What are RCD, RCBO and RCCB?
In modern life, electricity is everywhere. It brings us great convenience, but at the same time, it is accompanied by potential dangers. From daily household electricity use to industrial production, and from commercial places to public places, electrical safety has always been a crucial issue that cannot be ignored. Among the numerous devices that ensure electrical safety, RCD, RCBO and RCCB play a vital role. So, what exactly are RCD, RCBO and RCCB?
The Development History of RCD,RCCB,RCBO
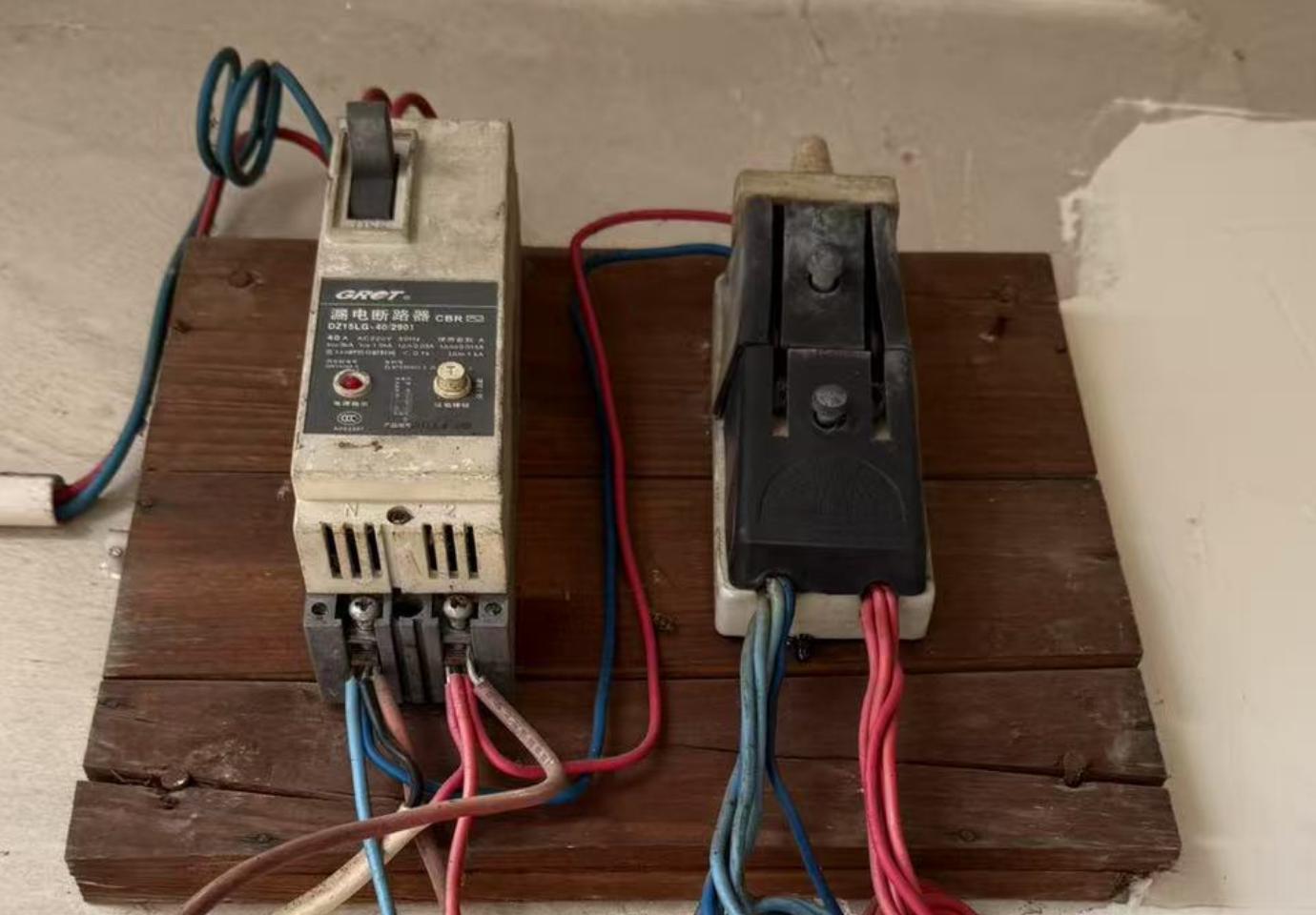

The picture above shows the leakage circuit breaker and knife switch that were used in China over a decade ago. This photo was taken in my old hometown house. For more than ten years, they have still been safeguarding the electrical safety of that old house.
In the early days, circuit protection mainly relied on simple fuses. When the current was excessive, the fuse element would melt, thus cutting off the circuit and providing protection. However, fuses could only protect against overloads and short circuits, and were ineffective in cases such as electric leakage. With the development of electrical technology and the continuous increase in people's requirements for electrical safety, various more advanced protection devices came into being.
The emergence of Residual Current Devices (RCD, RCCB, RCBO) has filled the gap in earth leakage protection. It can detect the residual current in the circuit. Once leakage occurs, it will quickly cut off the circuit to protect people from the risk of electric shock. However, when used alone, the RCCB cannot provide overload and short-circuit protection. Therefore, in order to meet the more comprehensive requirements of circuit protection, the RCBO, which combines the RCCB with a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB), came into being. It integrates the functions of overload protection, short-circuit protection, and earth leakage protection, and has become an important circuit protection device that is widely used today.
Application Scenarios of RCD
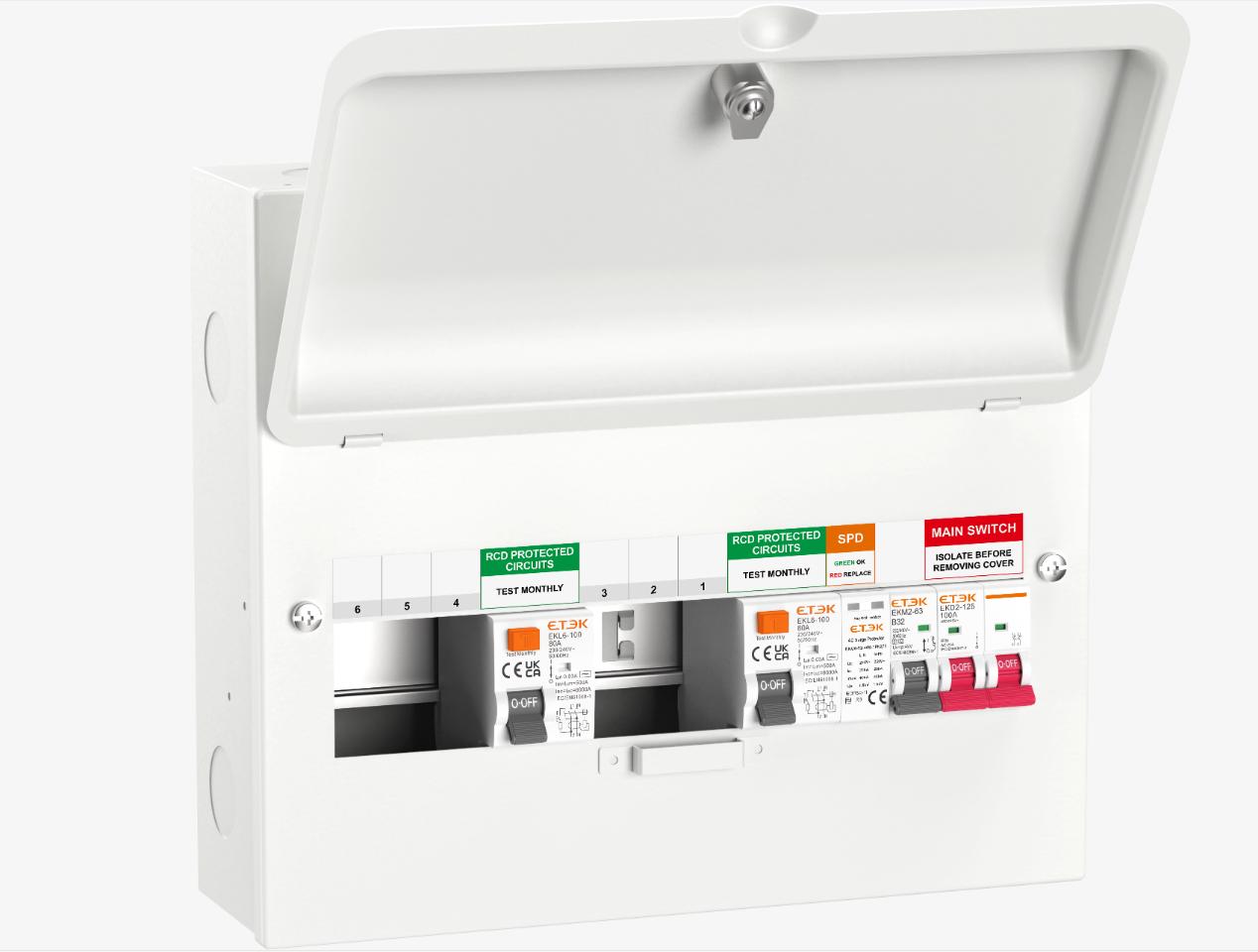
Residential Homes: There are numerous electrical appliances in households, such as refrigerators, televisions, air conditioners, electric water heaters, etc., and electrical safety is of utmost importance. The RCD is installed in the home distribution box, which can provide comprehensive protection for the circuits in each room. Whether it is electrical leakage of appliances, overloading during use, or short circuits caused by aging of the wiring, the RCD can promptly cut off the circuit, safeguarding the lives of family members and the integrity of the electrical appliances at home. For example, when the electric water heater leaks electricity, the RCD can act instantaneously to prevent the user from getting an electric shock.
.Commercial Premises: In commercial places such as shops, restaurants, office buildings, etc., electrical equipment is densely installed. The electrical load is relatively large and the usage time is long. Here, the RCD not only needs to ensure the normal operation of numerous lighting fixtures, computers, air conditioners and other equipment, but also deal with various possible electrical faults. Once electrical leakage or overloading and short circuit occur, the RCD can quickly cut off the faulty circuit, prevent the accident from expanding, and reduce commercial losses. For example, in a restaurant kitchen, a large number of cooking appliances are used simultaneously, which makes it prone to overloading. The RCD can protect the circuit in a timely manner.
Industrial Production: The industrial production environment is complex, with a wide variety of electrical equipment and high operating requirements. In factory workshops, from the drive motors of large mechanical equipment to various automated control systems, reliable circuit protection is indispensable. The RCD is capable of adapting to high currents, heavy loads, and complex electromagnetic interference in the industrial environment, providing stable power supply guarantees for industrial production. When the motor experiences overloading or short circuit faults, the RCD can quickly cut off the power supply, prevent equipment damage, and ensure the continuity of production.
.Public Places: In public places such as schools, hospitals, hotels, subway stations, etc., where there is a high density of people, the requirements for electrical safety are even stricter. When the RCD is used in the circuit systems of these places, it can ensure that the faulty circuit can be cut off in a timely manner under any circumstances, preventing large-scale casualties and social impacts caused by electrical accidents. For example, medical equipment in hospitals has extremely high requirements for the stability and safety of the power supply. The RCD can effectively protect the normal operation of these devices and safeguard the lives of patients.
Key Points for Selecting RCBO
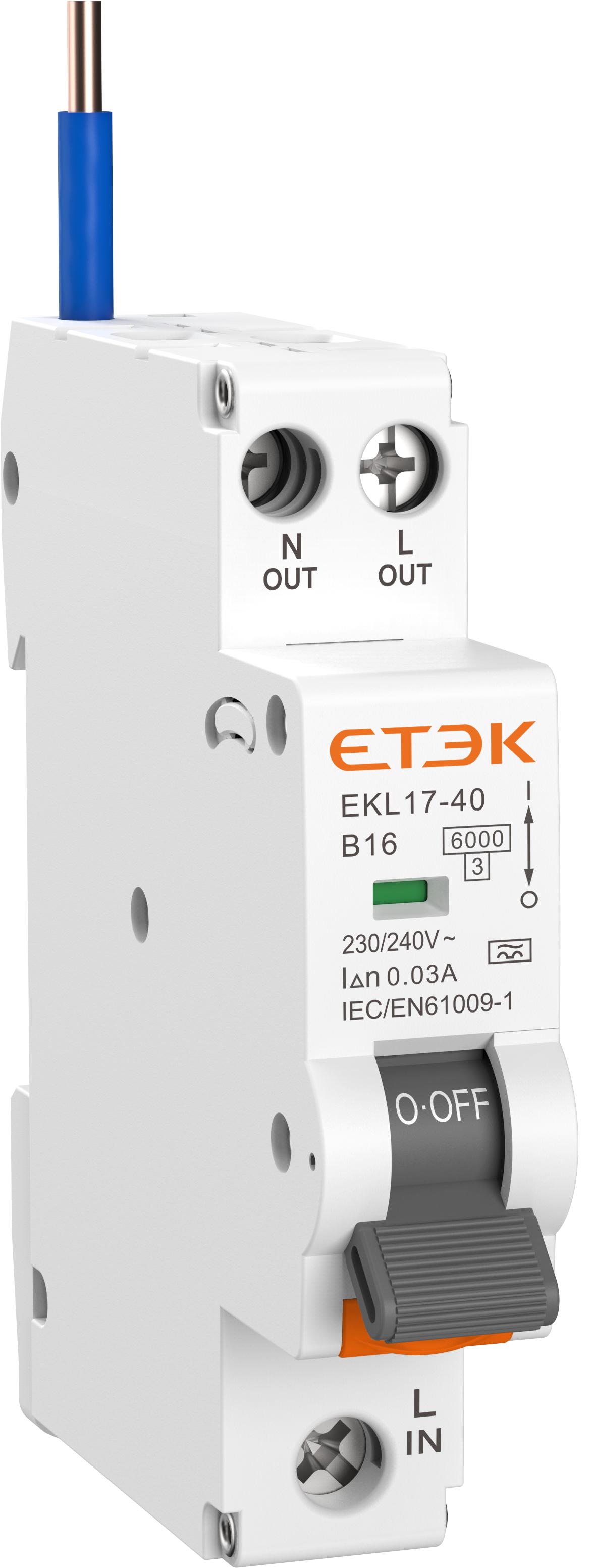

.1. Selection of Rated Current: Determine the rated current of the RCBO (Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent protection) according to the actual size of the electrical load. It is necessary to ensure that the rated current of the selected RCBO is greater than or equal to the total rated current of all electrical appliances in the circuit. At the same time, the possible peak values of instantaneous currents, such as the current during the starting of a motor, should also be taken into account. Generally speaking, the total current value can be obtained by dividing the total power of the electrical appliances by the operating voltage, and then the rated current can be selected with an appropriate margin.
.2. Selection of Residual Operating Current: The residual operating current is a key parameter for the leakage protection of the RCBO (Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent protection). For the protection against electric shock of people in general households and public places, an RCBO with a residual operating current of 30mA is usually selected. This can quickly cut off the circuit when a person gets an electric shock, ensuring personal safety. In some places that are more sensitive to leakage, such as operating rooms in hospitals, swimming pools, etc., an RCBO with a smaller residual operating current (such as 10mA) may be required. In industrial sites, according to the specific requirements of the equipment and the environment, the residual operating current may be selected as 100mA or even higher.
.3. Selection of the Number of Poles: The number of poles of the RCBO (Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent protection) mainly includes 1P+N and 3P+N. In a single-phase circuit, an RCBO with 1P+N is generally selected. The RCBO of 1P+N has widths of 18mm and 36mm, and it can disconnect both the live wire and the neutral wire simultaneously, which provides higher safety. In a three-phase circuit, according to the load conditions and the system grounding method, an RCBO with 3P+N is selected, which is suitable for situations where the three-phase load is unbalanced or the neutral wire needs to be protected.
4. Short-circuit Breaking Capacity: The short-circuit breaking capacity refers to the ability of the RCBO (Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent protection) to reliably cut off the short-circuit current under specified conditions. Different application scenarios have different requirements for the short-circuit breaking capacity. In households and some small commercial places, the short-circuit current is relatively small, and generally, an RCBO with a short-circuit breaking capacity of 4.5kA or 6kA can meet the requirements. However, in industrial sites or large commercial buildings, due to the large capacity of the power system, the short-circuit current may be relatively large, and an RCBO with a higher short-circuit breaking capacity (such as 10kA or even higher) needs to be selected to ensure that the circuit can be reliably cut off in case of a short-circuit fault, and to avoid equipment damage and the expansion of the accident.
.5. Magnetic Tripping Characteristics: The magnetic tripping characteristics of the RCBO (Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent protection) are similar to those of the MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker), and there are options such as B curve, C curve, D curve, etc.
B Curve:
Tripping Current: It usually trips instantaneously when the current is 3 to 5 times the rated current (In).
Application Scenarios: It is suitable for purely resistive loads and low-inductance lighting circuits, such as ordinary lighting circuits in households, electric heating equipment, etc. These loads have a relatively stable current during normal operation and a small starting current. The B-type tripping characteristic can act quickly when a relatively small short-circuit current occurs, protecting the circuit.
C Curve:
Tripping Current: It typically trips instantaneously when the current reaches 5 - 10 times the rated current (In).
Application Scenarios: This is the most common type, suitable for inductive loads and high - inductance lighting circuits. For example, household appliances like air conditioners, refrigerators, and washing machines, as well as electrical equipment in some small commercial places. These types of loads have a relatively large inrush current during startup, but the normal operating current is relatively stable. The C - type tripping characteristic can withstand a certain inrush current during startup and act promptly when a larger short - circuit current occurs, protecting the circuit and equipment.
D Curve:
Tripping Current: It trips instantaneously when the current is 10 - 20 times the rated current (In).
Application Scenarios: It is suitable for power distribution systems with high - inductance loads and large inrush currents, such as motors and transformers in industrial settings. These devices generate extremely large inrush currents during startup. The D - type tripping characteristic can adapt to such large - current surges, ensuring that there is no false tripping during normal device startup. Meanwhile, it can quickly cut off the circuit in case of faults like short - circuits, protecting the equipment and personnel safety.
There are also some special curves that will not be introduced here. If you have such needs, you can contact ETEK Company for customization.
Selection of Leakage Current Type: The types of leakage currents mainly include AC type, A type, B type, S type, F type etc. The A-type RCBO (Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent protection) can operate reliably for both sinusoidal alternating current leakage currents and pulsating direct current leakage currents, and it is suitable for common households as well as general industrial and commercial environments, covering most of the leakage scenarios of daily electrical appliances. The AC-type RCBO is only effective for sinusoidal alternating current leakage currents and is usually used for the protection of some specific pure alternating current circuit devices with relatively simple leakage conditions. When selecting the type, it is necessary to determine the appropriate leakage current type according to the characteristics of the actual electrical equipment and the environment. For example, if there are many electronic devices in the place, and the leakage currents they generate may contain pulsating direct current components, it is more appropriate to select an A-type RCBO at this time; if it is just a simple pure alternating current load circuit such as lighting, an AC-type RCBO may be able to meet the requirements.
RCDs of ETEK
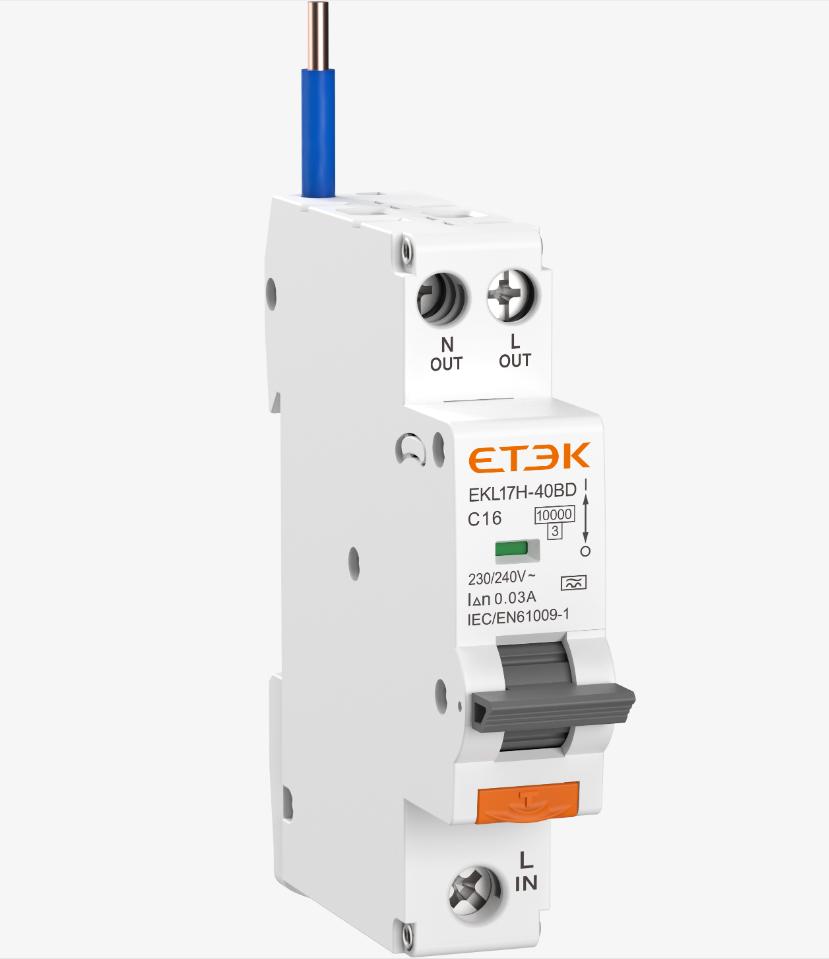

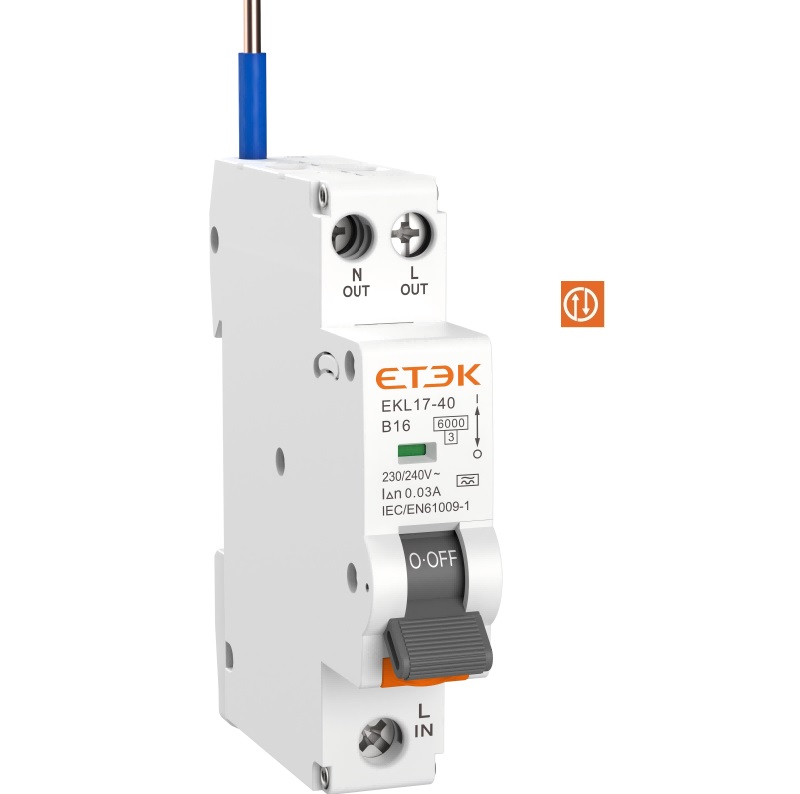
Bidirectional wiring RCBO EKL17 series
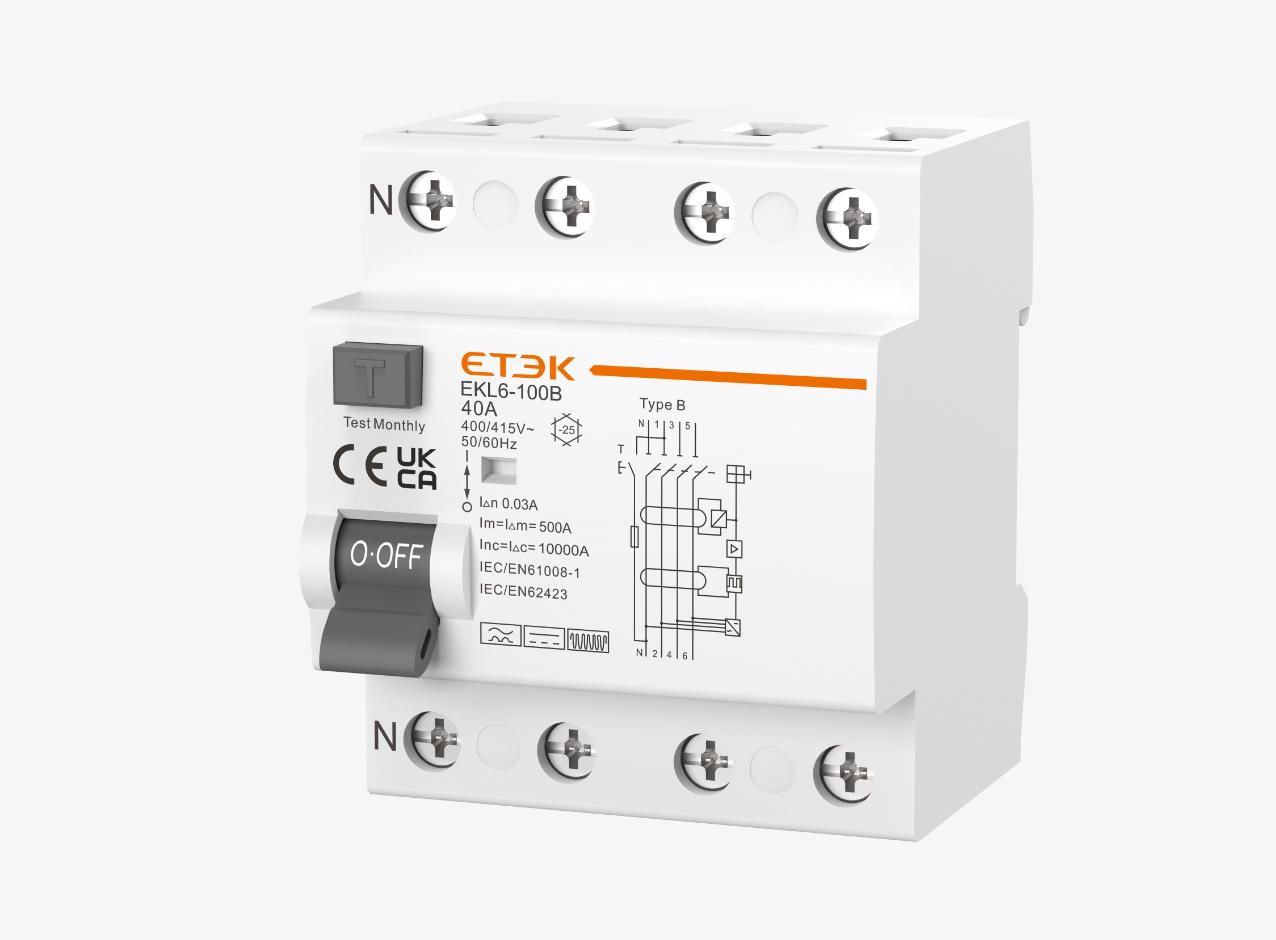

Electromagnetic Type B RCCB EKL6 Series
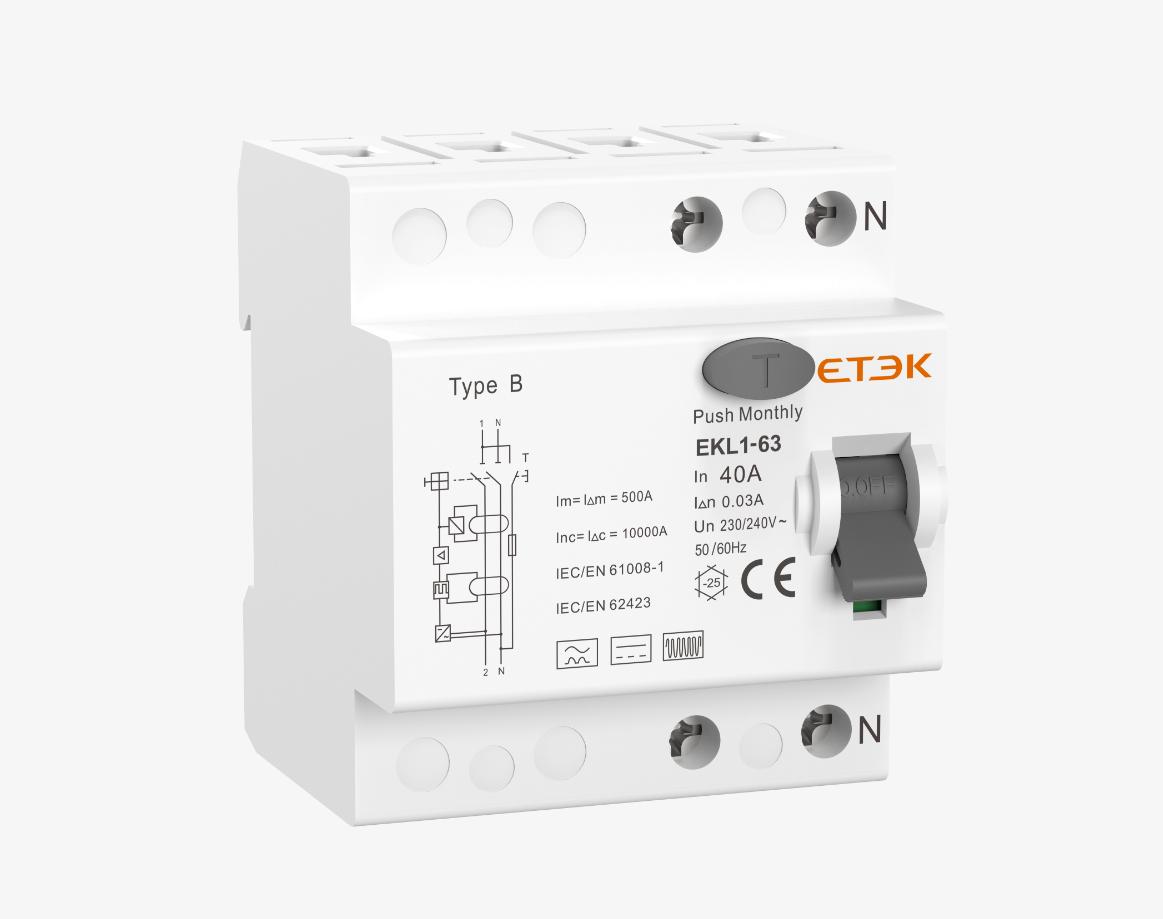

Electromagnetic Type B RCCB EKL1 - 63 Series
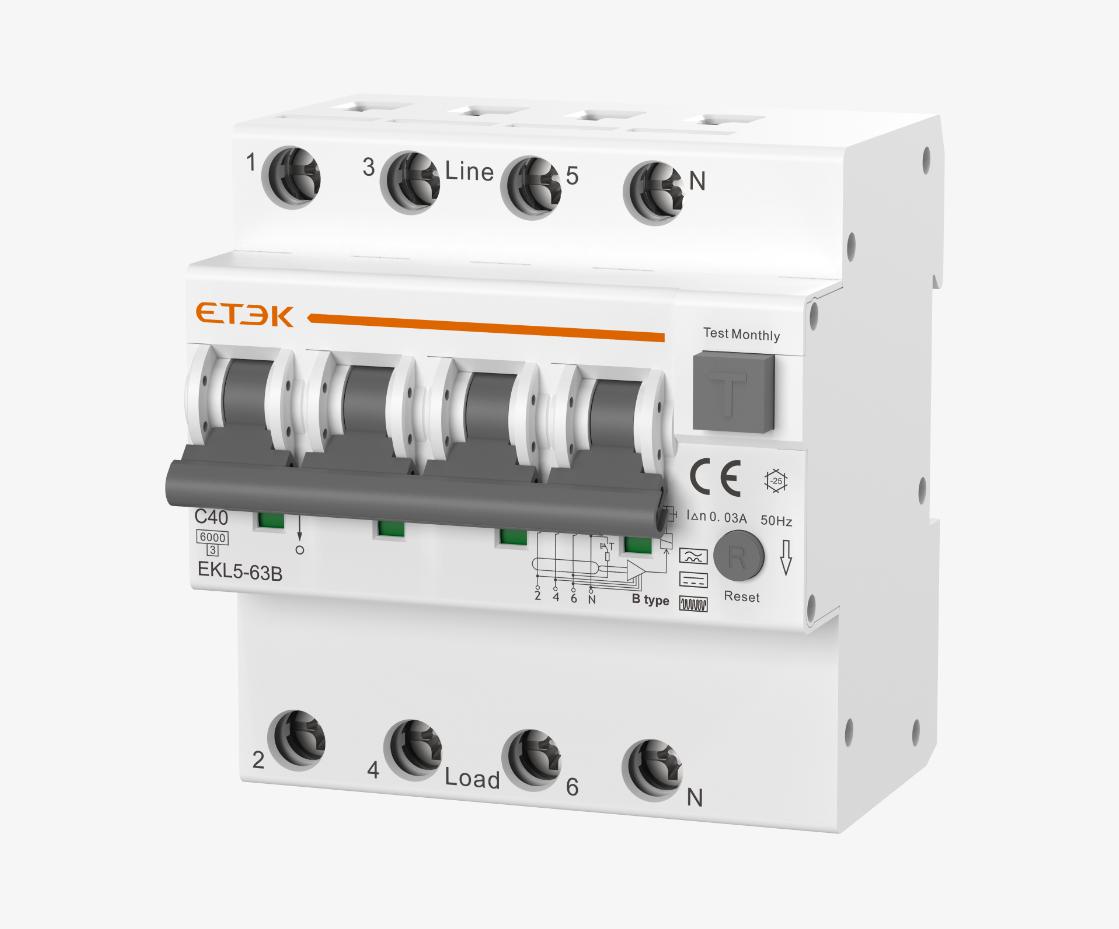

Electronic Type B RCBO EKL5 - 63 Series
More detial check
Zhejiang ETEK Electric Technology Co., Ltd.,has always been committed to the research, development and production of electrical safety equipment, and has unique advantages in the field of RCDS products. ETEK has both electronic and electromagnetic residual current circuit breakers, and also owns the bidirectional wiring RCD which is rare in the market. Traditional RCDs have certain limitations in terms of wiring, while our bidirectional wiring design makes the installation more flexible and convenient. Whether in a distribution box with limited space or in some special wiring scenarios, the bidirectional wiring RCD can easily cope with it, greatly improving the installation efficiency and reducing the installation costs and time costs caused by difficult wiring. We always adhere to quality as the core, and strictly control every link, from raw material procurement to production and processing, and then to finished product inspection. Through advanced production processes and strict quality control systems, we ensure that every RCBO product leaving the factory has reliable performance and stable quality. Choosing ETEK means choosing a more reliable guarantee for electrical safety, creating a safe and stable electrical environment for your life and work. We hope that through today's introduction, you have gained a certain understanding of RCDs, and also have a better understanding of ETEK. In the next issue, we will provide a comprehensive and detailed introduction to all ETEK RCD products. If you have any needs in terms of electrical safety, you are welcome to contact us at any time. Let's work together to contribute to electrical safety!
























